Table Of Content

"The rib vault, flying buttress, and pointed (Gothic) arch were used as solutions to the problem of building a very tall structure while preserving as much natural light as possible," according to Brittanica. The best-known examples of Gothic architecture still standing today include medieval buildings as well as those built during the Gothic Revival period. Germany's Ulm Minster, for example, was begun in the 1300s but not completed until the 1800s. And Paris's beloved Notre Dame is undergoing yet another rebuild—which may be the tenth in its history—following a tragic fire in 2019. It's no question, these grand buildings take vast resources (both manpower and money) to complete, and they're monuments to the communities they serve.
Military architecture
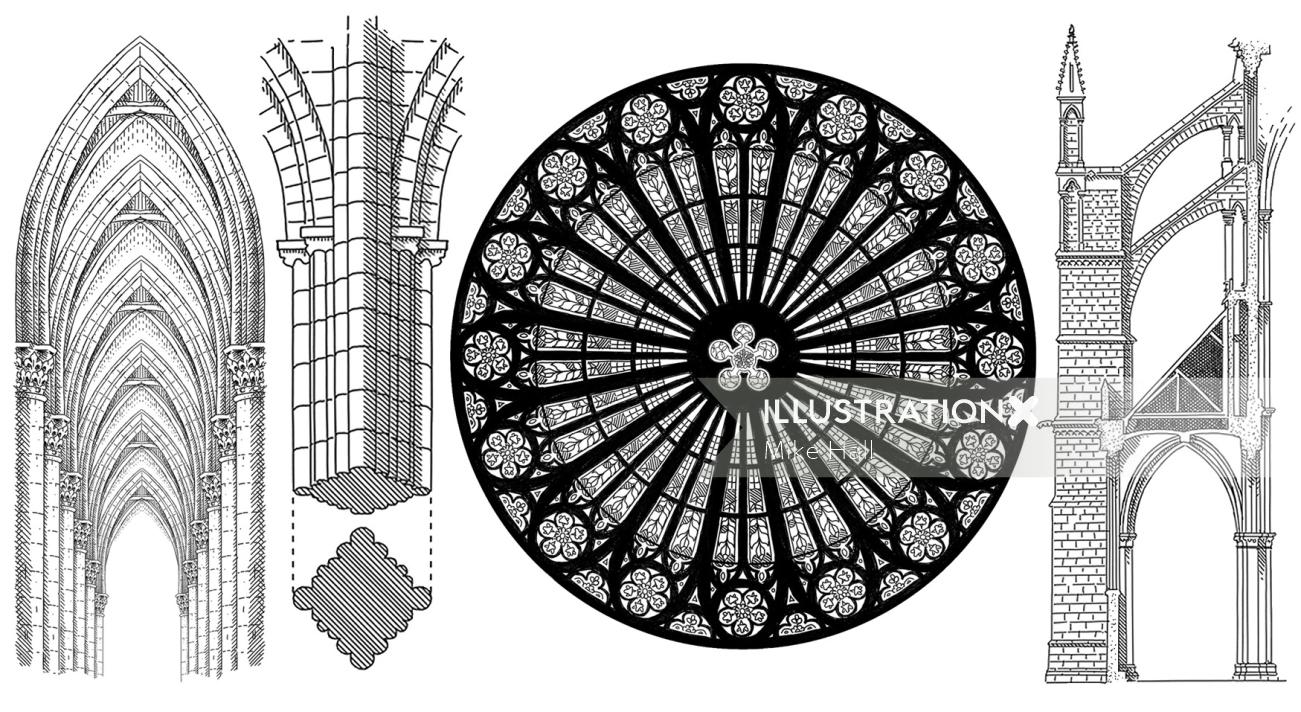
(the above photo was taken before the fire) Today there is an ongoing restoration project to rebuild Notre-Dame de Paris in its original form. The pointed arches of the early Gothic period were narrow windows terminating in a lancet arch (lancet windows).In the later periods, these pointed arches were of different sizes and decorated with sculptures. Rather than the rounded arches typical of the earlier Romanesque style, Gothic architecture is known for arches that come to a steep point. Gothic pointed arches, inspired by Islamic architecture, point to the heavens and accentuate the ultra-tall ceilings.
Garment Capitol Building
Spring Grove Cemetery is a window to Cincinnati's Gothic past - The Cincinnati Enquirer
Spring Grove Cemetery is a window to Cincinnati's Gothic past.
Posted: Sat, 07 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
In the Renaissance, Gothic fell out of favor as classical symmetry and proportions were revived. But Gothic had a major revival starting in the mid-18th century in Britain, inspiring the Gothic Revival across Europe and America into the early 20th century. Features like pointed arches, rib vaults, and stained glass were recreated in Neo-Gothic buildings like Britain’s Houses of Parliament. The Gothic style also influenced the 19th-century Romantic movement that emphasized emotion over reason. Gothic’s soaring structures and mysterious aesthetics appealed to Romantic artists and writers. One of the most important technical innovations from the Gothic Age was the Flying Buttress.

Characteristics of Gothic Architecture
These include embellished colonnades and colonettes, sculptural moldings, statues of saints and historical figures, pinnacles and spires, and gargoyles, grotesque figures that double as water spouts. The pointed arch was a noted element of Middle Eastern architecture beginning in the 7th century, as seen in the Al-Aqsa Mosque (780) in Jerusalem. Widely deployed in the building of mosques and palaces like the fortress of Al-Ukhaidir (775), the pointed arch was found throughout the Middle East, North Africa, Andalucia (modern day Spain), and Sicily.
The Quintessence of Gothic Architecture
In one particularly startling juxtaposition, she shows the architectural similarities between London’s iconic Big Ben and the minaret from the Great Mosque of Aleppo in Syria (an Umayyad building). Both are squared off towers that rise in four sections, and both are decorated with similar elements, such as trefoil arches. While not specifically a Muslim innovation (isolated examples existed in locations around Persia and Syria prior to the advent of Islam), its use was spread far and wide via Muslim religious shrines such as Al Aqsa.
Designed by Arnolfo di Cambio, construction started in 1296 and finished in 1436. Pink and green shades of polychrome marble were used for the exterior of the church and the facade is created in the Gothic revival style. This massive and beautiful Gothic cathedral is situated in the city of Cologne in Germany. This revered monument of Catholicism in Germany is also the seat of the Archbishop of Cologne and was designed by Master Gerhard, as well as further designs through the years by Ernst Friedrich Zwirner and many others. It would remain incomplete for more than 350 years until work once again resumed in the 1840s.
Some of the key elements of Gothic architecture—like large, stained glass windows and vaulted arches—allowed ample natural light into the structures, despite their massive size and height. This style dominated European architecture—especially structures built by the Roman Catholic church—until the 16th century, when it became known as Gothic architecture. Check out the sides of a Gothic building to see these architectural features in action. Medieval architects had to figure out a way to support the massive weight of stone Gothic structures as the pressure was on to construct ever bigger, taller, grander churches.
The entire front facade, the bell tower, the nave, and all of the stained glass date to the late 13th-15th century. Strasbourg even held the title of “Tallest Building on Earth” from 1647 to 1874, after the collapse of another church’s belltower in 1647. One final element that can be seen throughout the Gothic Buildings of Europe is vertical emphasis, with lots of towering forms and spaces that are disproportionately tall when compared to their floor area. Palma Cathedral in Spain has one of the tallest naves ever constructed during the Gothic Age, and the church’s entire design revolves around this soaring central space. The arms race to build taller and taller buildings led to several world records during the gothic age.
The nave is 121 feet (37 m) tall, and the taller of the two towers measures 371 feet (113 m) tall. Completed in the early 13th century, Chartres Cathedral was built in the first part of the Gothic Age. The city of Chartres has a very well preserved medieval center, so the church and its surroundings look the same as they did centuries ago. A unique form of English fan vaulting features a dense cluster of thin ribs that spread out from each column, resembling an inverted, curved cone. The walls are completely dissolved in glass, and the vaults, windows, and detailing are in complete harmony with this technique of fan vaulting.
First and foremost they developed a ribbed vault, in which arching and intersecting stone ribs support a vaulted ceiling surface that is composed of mere thin stone panels. The round arches of the barrel vault were replaced by pointed (Gothic) arches which distributed thrust in more directions downward from the topmost point of the arch. New churches in the Neo-Gothic style were also built like Saint Clotilde Basilica (1857) in Paris.
Gothic architects also used wood for essential structural elements like roof trusses. Wooden centering aided in constructing intricate stone vaults built piece by piece. Gothic architecture is distinguished by characteristics, most notably the pointed arch, rib vault, flying buttress, extensive use of stained glass, tall spires, and elaborate decorative carvings. The pointed arch distributed weight more effectively than the rounded Romanesque arch, allowing walls to be thinner and windows to be much larger with minimal support.
Often incorporated with arches of varying sizes connecting to different structural levels, Gothic architecture shapeshifted towards flying buttresses. With flying buttresses in the structure, the architects and designers were able to expand the construction scope without using thick walls. Although it can’t be proved, many historians argue that Lincoln Cathedral was once the tallest structure ever built after its central tower was completed in 1311. But unfortunately, the central spire atop the tower collapsed in the 16th century, therefore dethroning the church as the world’s tallest building. Despite the collapse of the tower, the church is still one of the most vertically impressive in England.
Martini’s works, employing an elegant sense of line and refined decorative effect, as seen in his Maestà (1315), influenced the International Gothic Style. Gothic architecture retained the Romanesque western façade as the entrance to the church with its two towers, three portals and sculptural works in the tympanum, a half circle area above the door, as well as its cruciform plan. While Gothic churches continued the religious tradition of the pilgrimage path, their new style reflected a new economic and political reality. The central panel depicts the Annunciation, when archangel Gabriel, carrying an olive branch, kneels before Mary, darkly robed on the right, and informs her that she will give birth to the son of God.
It was both a decorative and practical element of history and was elaborately designed. The Basilica Church, founded as Abbey of Saint-Denis, was regarded as the first gothic building, and it marks the evolution styles out of Romanesque. The Basilica of Saint-Denis had two towers of similar height on the west front, and this is a plan that was imitated in the plan for Notre-Dame de Paris. For the longest time, these enormous Gothic cathedrals were the city's landmarks before modern tall buildings.
During the Renaissance period, five bells were installed in the cathedral, which was tuned to E flat. The cathedral was ordered to be demolished by German forces during World War II but refused direct orders to do so. During another period of invasion in the city locals burnt down their shops before the invading Soviet troops could enter the city. A unique feature of the church is its multi-colored tile roof, which has helped the famous building become one of the most recognizable structures in the city. During that time many beautiful examples of Gothic cathedrals and buildings have been designed and constructed around the world.
Natural light streaming through colorful glass makes for an ethereal, uplifting environment. Modern architects can emulate this effect using skylights, clerestories, expansive glass walls, or stained glass elements. Ornamentation defines Gothic buildings, from elaborate sculptural programs to stone tracery, pinnacles, and gargoyles. Contemporary architects can nod to this decorative legacy with artistic façade treatments, creative use of materials, or commissioned artworks integrated into their designs. This legacy of ambitious experimentation and pushing boundaries can continue to inspire architects today.